Structure and Function of the Brain

The entirety of this site is protected by copyright @ 2010-2023 G-Code Consultancy
G-Code Consultancy
Decipher Your Genetic Code
"Twentieth-century is the age of genes; The twenty-first century is the age of the brain". Humans have a very dedicate system incprocessing information, presenting themselves with characterirsitcs of accuracy, sensitveness, speed and efficiency.
All of these characteristics are controlled by the nervous system, especially the brain.
The brain is the control center of the body. Besides, it is also a vast and complicated automatic controlling system that interprets messages.
The brain, the foundation of human intelligence, is where thinking and consciousness occur. Also, the brain is a highly flexible and quickly adjusting mechanism. It can learn from various environments and experiences.
Challenging the research and development of neuroscience is in modern science, and it deserves serious attention. Not only is a neuroscience-based on scientific theory, but also filled with practical social meanings.
As the most complex organ in the body, the brain consists of 50 to 100 billion neurons. The cerebral cortex is the essential part of the brain that makes human beings unique.
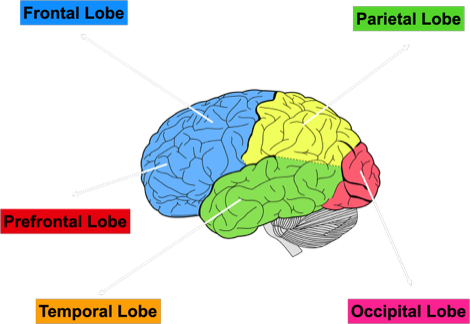
The cerebral cortex has several bumps and grooves known as gyri and sulci, increasing the cerebral cortex's surface area. Medical experts usually divide the cerebral cortex into four lobes: Frontal, Parietal, Temporal, and Occipital Lobes.
They are large areas of the brain with different positions and functions. These functions range from reasoning, language to auditory perception.
The Frontal Lobe is located in the front part of the brain. It is the most prominent lobe in healthy human brains. The frontal lobe extends back to a fissure callede the dentral sulcus, which separates the front lobe from the parietal lobe. It can receive information signals from other lobes of the brain. This lobe is associated with decision-making, cognition, reasoning, expressive language, and regulating social behaviour.
The Prefrontal Lobe is a part of the brain located at the front of the frontal lobe. This brain region has been implicated in planning complex cognitive behaviour, personality expression, decision making, moderating social behaviour and greatly contributes to personality development.
The Parietal Lobe is located in the middle section of the brain above the occipital lobe and behind the frontal lobe. Although it is the brain's most minor lobe, the parietal lobe plays a vital role in sensory perception and integration.
The parietal lobe helps integrate sensory information, including pressure, pain, touch, and temperature. You can still receive the information from your ears, eyes, and other sensory organs without the parietal lobe. But you might not be able to make sense of the information or meaning to it.
The Temporal Lobe is located below the parietal and occipital lobes, on the bottom of the brain below the lateral fissure. There are two temporal lobes close to the ears on both sides of the brain.
Temporal Lobe plays a key role in auditory processing, including receiving sound signals and processing signals' meaning. The temporal lobe is also responsible for converting short-term memories in the hippocampus and amygdala into long-term memories and processing new information with them.
The Occipital Lobe is located above the temporal lobe and beneath the parietal lobe. It is located in the cerebral cortex region and sits at the back portion of the brain.
The occipital lobe is the brain's processing hub responsible for processing visual information. The study found that visual processing is the most significant function of the occipital lobe.